Can you reverse your age naturally?
Overview
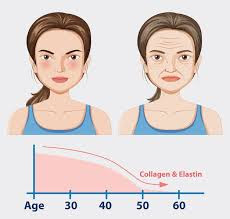
Science shows how simple lifestyle modifications can reverse aging naturally. What if wrinkles, weakness, and age-related problems weren't inevitable? Recent longevity research suggests this. The intricate process of aging begins and progresses. Although you can't stop it, research reveals modest but effective lifestyle changes can reverse aging. However, lifestyle modifications can help you live longer and healthier.
Here are some ways to appear and feel younger:
- Eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins for a healthy diet. Eat nuts, seeds, turmeric, and green tea to reduce inflammation.
- Drinking water keeps your skin and body moisturized, making you seem younger.
- Stay Active: Exercise regularly with yoga, swimming, walking, or strength training to maintain muscular tone and flexibility.
- Quality sleep helps your body heal and revitalize. Manage stress with meditation, mindfulness, or hobbies.
- Chronic stress speeds aging.
- Skin care: Use sunscreen, moisturize daily, and use natural products to keep your skin healthy.
- Maintain a positive outlook and enjoy life. Well-being improves with happiness.
- Drink less, smoke less, and avoid environmental contaminants.
- Build Social Connections: Spend time with loved ones to improve emotional well-being.
- Stay Curious: Never stop learning new skills or hobbies. You can't turn back time, but these tips can make you look and feel younger.
What is the aging process?
Aging is a normal and complex process that involves gradual physiological and cellular changes. Though universal, the changes and their rate vary by person.
General overview:
- Cellular changes: Cells divide and heal less efficiently over time. DNA damage and telomere shortening cause cell aging and death.
- Tissue and Organ Changes: Aging cells may lose function. Skin may lose suppleness and moisture, bones may become less thick, and organs, including the heart and kidneys, may decline.
- Age-related metabolic shifts affect energy levels and body composition (e.g., increased fat and decreased muscular mass).
- Impairment of the immune system makes older people more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Oxidative Stress: Metabolism produces unstable chemicals called free radicals, which harm cells and age them. Without antioxidants, this damage builds up.
- Estrogen, testosterone, and growth hormone levels drop, influencing reproduction, mood, and energy.
- Cognitive and Neurological Changes: Aging can slow processing, impair memory, or cause neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's.
- Aging is inevitable, but a healthy lifestyle, including excellent nutrition, exercise, and stress management, can reduce its effects and improve quality of life.
How can aging affect mental health?
Aging affects mental health differently based on lifestyle, circumstances, and physical health. Aging may affect mental health:
Changes in cognition:
- Age-related cognitive decline can cause slower processing speeds, shorter attention spans, and moderate memory lapses in older persons.
- Dementia and Alzheimer's disease can cause severe cognitive deficits.
Emotional Wellness:
- Aging can increase vulnerability, worry, and stress, especially over health, finances, and independence.
- Many older persons report enhanced emotional stability and resilience, valuing meaningful connections and experiences.
Depression/Anxiety Risk:
- Retirement, loss of loved ones, and social isolation can cause grief or worry.
- Chronic illnesses or physical limits can worsen these emotions, producing a mental misery cycle.
Social isolation and loneliness:
- Reduced mobility or family changes can limit social interactions, causing loneliness and mental health issues.
- Socializing greatly reduces these consequences.
Positive Growth:
- Contrary to preconceptions, many people discover meaning and purpose in later life by trying new interests, building relationships, or volunteering.
- Wisdom and life experience can boost self-acceptance and fulfillment.
Age-related mental health difficulties are also opportunities for personal growth and contemplation. Staying active, having strong social relationships, and getting professional care when needed promote mental health.
The video explains how to reverse your age
How do social relationships affect mental health with age?
- As we age, social ties are essential to mental health. This is how strong social relationships improve mental health:
- Combat Loneliness: Social contacts reduce loneliness and isolation, which can lead to depression and anxiety in older persons.
- Emotional Support: Talking to others and sharing experiences gives comfort and belonging. This can help people cope with retirement, illness, and loss.
- Conversations and social activities stimulate the brain, minimizing the risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
- Stress Reduction: Positive social interactions increase oxytocin, which relaxes and connects.
- Sharing happiness, laughter, and meaningful experiences with people boosts mood and contentment.
- Friends and family encourage healthy habits, including exercise, eating, and medical exams.
- Sense of Purpose: Community and family provide people a reason to stay active, improving mental health.
As we age, socializing with friends, family, community groups, or volunteering can improve quality of life and mental health.
No comments:
Post a Comment