Genital warts may lead to cervical cancer.
Overview
Skin infections called warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Common warts, plantar warts, flat warts, and genital warts are among the several varieties of HPV that cause these lesions. There are over 100 different forms of HPV.
Warts are common, particularly in young children. It is estimated that up to one in five children will get warts, with children between the ages of 12 and 16 having the highest incidence. Many wart infections resolve without the need for medical attention. A wart is the outcome of the virus's rapid growth of skin cells when it infects the epidermis' outermost layer.
The following are important facts regarding warts:
- Transmission: Direct contact with a wart or anything that has come into contact with one, including towels or razors, can spread HPV.
- There are various types of warts, including common, plantar, flat, and genital warts.
- Risk factors: Children, people with compromised immune systems, and people with long-term skin disorders are more likely to develop warts.
- Prevention: Keep your skin fresh and clean, stay away from direct contact with warts, and refrain from sharing personal objects like razors and towels.
Symptoms of warts
Warts can have many different shapes depending on their nature and where they are on the body.
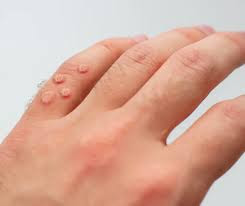
Common warts develop on the hands and fingers. These are tiny, rough-feeling skin growths that are gritty. Tiny black spots, which are occluded blood vessels, may be present.
Plantar Warts: The soles of the feet are home to these excruciating warts. The pressure from standing and walking causes them to frequently develop inward, covering the wart with a thick layer that resembles a callus.
Flat warts: Compared to other kinds of warts, they are smoother and smaller. They typically show up on the face, neck, or frequently shaved areas. They may be slightly yellow, brown, or pink.
Filiform Warts: These are tiny warts with projections that resemble fingers. They frequently show up on the nose, eyes, lips, or face.
Genital warts: These are found in the anal and genital areas. They may resemble cauliflower or be tiny, flesh-colored lumps. They could make you uncomfortable or itchy.
For an accurate diagnosis and course of treatment, it's wise to see a healthcare provider if you observe any odd growths on your skin.
Factors contributing to wart risk
Several conditions can increase the risk of developing warts. These are a few typical risk factors:
Weakened Immune System: Warts are more common in those with compromised immune systems, such as those living with HIV/AIDS or using immunosuppressive medications.
Age: Because their immune systems are still developing, children and teenagers are more susceptible to warts.
Damage to the Skin: Cuts, scrapes, and other skin injuries can allow the human papillomavirus (HPV), the cause of warts, to enter the body.
Personal Contact: The risk of transmission may be increased by coming into close contact with a person who has warts or by touching objects (such as towels or razors) that have come into contact with warts.
Wet Environments: The risk of developing warts can be raised by spending time in wet areas, such as public swimming pools or shared showers.
Cuticle picking and nail biting are two behaviors that can lead to tiny skin cracks, which facilitate the virus's entry and development of warts.
Therapy.
There are several treatment options depending on the type, location, and severity of the wart. Here are a few typical therapies:
Salicylic acid, which is frequently found in over-the-counter medications, aids in the removal of diseased skin. Since it may take a few weeks for the wart to go away, it's crucial to pay close attention to the directions and exercise patience.
Cryotherapy is the process of freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is typically administered by a medical expert. It can be uncomfortable and may take several sessions.
Prescription Drugs: A doctor may recommend more potent therapies, like topical creams containing retinoids or immune system boosters, for warts that are difficult to get rid of.
Laser Treatment: In this technique, the wart is burned away using a laser. It is typically used on warts that have not responded to traditional treatments.
Surgical Excision: In some cases, a doctor may suggest removing the wart surgically. This is typically considered a final option due to the potential for scarring.
Home Remedies: For certain patients, duct tape occlusion therapy—which entails wrapping the wart in duct tape for a few days, then taking it off, soaking it, and filing it down—works effectively.
It's wise to speak with a medical expert to find the best course of action for your particular circumstance.
The genitalia's warts
Genital warts are a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Warning:
Go to the doctor if you think you might have genital warts so they can prescribe medication. It is not advisable to just wait for genital warts to go away.
To detect cervical cancer, a cervical screening test should be performed on adults who have genital warts.
The following are important facts about genital warts:
Appearance: They frequently resemble cauliflower or are tiny, flesh-colored lumps. They are located around the anus, on the genitalia, or in the pubic region.
Transmission: During vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse with an infected individual, genital warts can spread by skin-to-skin contact. The infected person can still spread the virus even if they don't exhibit any symptoms.
In addition to the obvious warts, other symptoms may include bleeding during intercourse, pain, and itching. Some people, nevertheless, might not even have any symptoms.
Therapy:
Although HPV cannot be cured, the warts can be removed with treatment. Topical drugs, laser therapy, cryotherapy (freezing the warts), and surgical excision are among the available options.
Prevention:
Although using condoms helps lower the risk of transmission, not all potentially contaminated places are covered by them. There are vaccines to guard against the most prevalent HPV strains that cause genital warts and some types of cancer.
How to stop new warts from appearing and speed up their healing
Here are some suggestions to speed up wart healing and stop new ones from appearing:
Resolving Warts:
- Get Rid of the Wart Faster: Salicylic acid-based over-the-counter remedies can aid in the removal of the diseased skin. It can take a few weeks, so have patience.
- Cryotherapy is the process of freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. It may take several sessions and is often performed by a medical expert.
- Cover the Wart: You can reduce the risk of the virus spreading to other parts of your body or other people by covering the wart.
- Steer clear of shaving over warts because doing so can result in small cuts on your skin, which could let the virus spread to other areas of your body.
How to Stop New Warts
- Don't Touch Warts: Because HPV is contagious, don't touch other people's warts.
- Individual cleanliness: Make sure that every household member has their items, such as towels, washcloths, and a razor.
- Clean and Cover Cuts: Keep cuts and scrapes clean and covered because HPV can enter via them.
- Wash Your Hands Frequently: Handwashing regularly aids in the virus's removal from your skin.
- Avoid Dry, Cracked Skin: Keep your skin hydrated to avoid fissures that could let the virus in.
- Quit biting your nails and chewing your cuticles because these habits can lead to microscopic skin tears that allow the virus to enter your body.
By following these tips, you can reduce the likelihood of developing new warts and hasten the healing of existing ones.
Two methods to hasten the healing of warts
Look after the wart.
When a person's immune system is strong, a wart will often go away on its own.
This could take a while, though. In the meantime, the virus that causes warts might spread to other parts of the body, possibly leading to more warts. With treatment, a wart may disappear more quickly.
You can buy an efficient wart cure without a prescription. When treating a wart, dermatologists recommend the following actions:
Make sure your wart is covered.
This reduces the likelihood that the virus will spread to other people and bodily parts. Wash your hands as soon as you come into contact with the wart.
Additionally, this reduces the likelihood that the virus will spread to other people and parts of the body.
You should not shave over a wart. When you shave, tiny tears are created in your skin. Shaving over the wart will result in microtears on both the shaved skin and the wart itself. These microtears allow the virus that causes warts to spread from the wart to any skin you shave.
For example, shaving over a wart and then shaving his face can cause new warts to appear where his beard was. If a woman shaves over one wart and then shaves her legs, she may get several. You may get warts in your pubic area if you shave over a wart and then shave your pubic hair.